What Gets Paid First on an Amortization Schedule? Discover the Order
The principal balance on an amortization schedule is the first thing that gets paid. An amortization schedule is a financial tool that outlines the repayment of a loan over time.
It shows how much of each payment goes towards interest and how much goes towards principal. This schedule is an essential tool for borrowers to understand how their payments are divided and when the loan will be fully paid off.
By following the schedule, borrowers can ensure that they are consistently paying down the principal balance and reducing their overall debt. Understanding the key components of an amortization schedule can help borrowers make informed decisions about their loan repayments and financial future. So, let’s take a closer look at what gets paid first on an amortization schedule.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Amortization_Final_4201631-42b04cd2ad724b96af0c5e8f8fded072.jpg)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
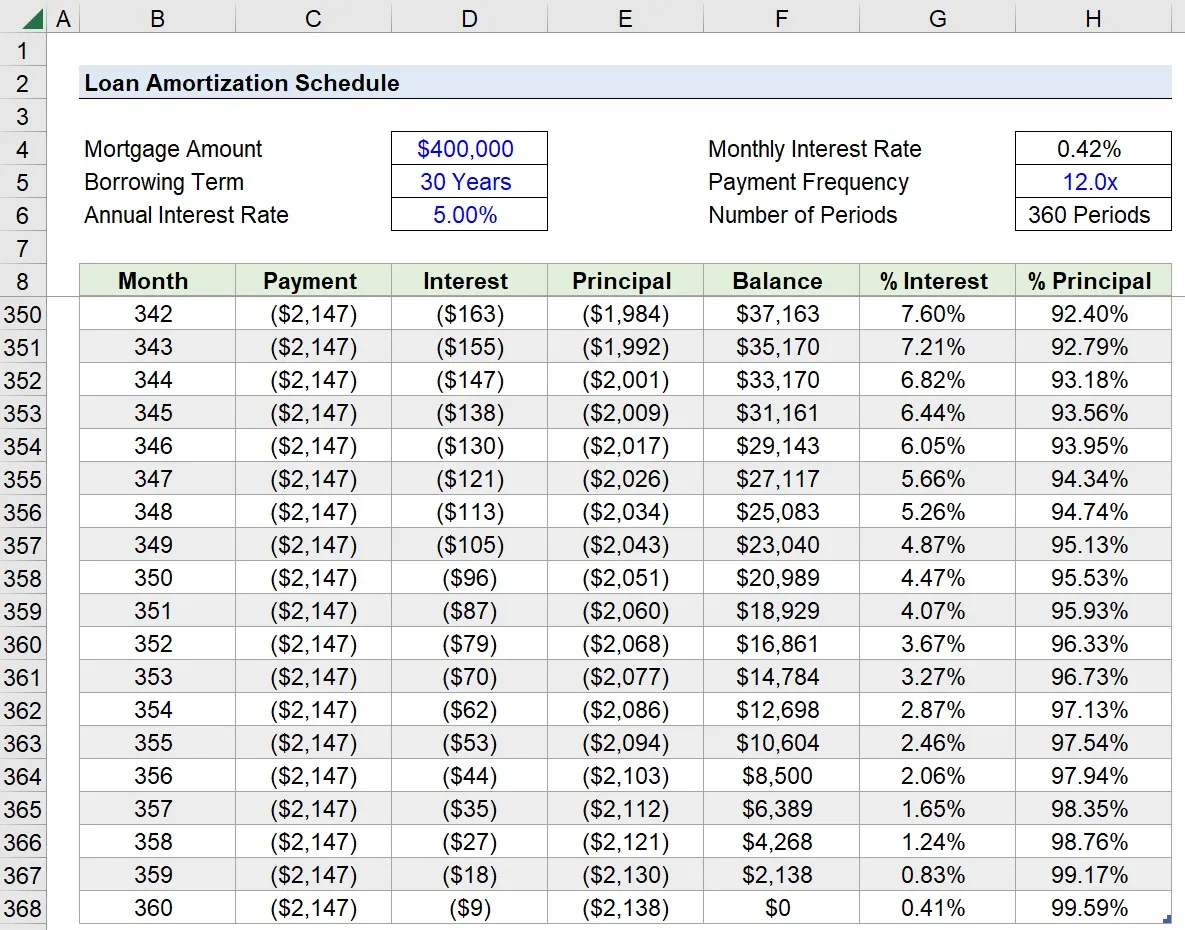
Understanding Amortization Schedule
In an amortization schedule, the initial payments primarily go towards interest, with a smaller portion allocated to the principal. As the schedule progresses, the proportion of the payment dedicated to the principal gradually increases while the interest portion decreases. This process allows for the timely reduction of the loan balance.
Understanding Amortization Schedule Definition An amortization schedule is a detailed table that outlines the repayment plan for a loan, including the principal amount, the interest rate, and the length of the loan. This schedule allows borrowers to understand how their payments are allocated between the principal and interest over the life of the loan. By analyzing an amortization schedule, borrowers can gain a clear picture of how their debt is being paid off over time. Key Components 1. Principal Amount: The principal amount is the original loan balance that the borrower has taken out. This is the initial amount that needs to be repaid to the lender. 2. Interest Rate: The interest rate is the percentage charged by the lender for borrowing the money. It is important to remember that a higher interest rate will result in higher interest payments over the life of the loan. 3. Loan Term: The loan term is the length of time that the borrower has agreed to repay the loan. It is typically expressed in months or years. A longer loan term means smaller monthly payments, but it also means that more interest will be paid over time. 4. Monthly Payment: The monthly payment is the amount that the borrower needs to pay each month to satisfy the loan obligation. This payment is composed of both principal and interest and is calculated based on the loan amount, interest rate, and term. 5. Amortization Table: The amortization table is the heart of the amortization schedule. It provides a month-by-month breakdown of the loan payments, showing the amount applied to principal and interest for each payment. This table is extremely useful for borrowers to track and understand how their debt is being paid down. In summary, an amortization schedule gives borrowers a transparent view of their repayment plan. By understanding the key components of this schedule, borrowers can gain insights into how their payments are allocated between principal and interest. This knowledge can empower borrowers to make informed decisions about their finances and stay on track with their repayment schedule.Prioritizing Payments
When it comes to managing your finances and paying off debts, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of what gets paid first on an amortization schedule. An amortization schedule outlines the breakdown of your monthly payments, determining how much goes towards principal, interest, and any fees or charges. By understanding the order in which these payments are prioritized, you can make informed decisions to effectively manage your debt.
Principal
The principal is the initial amount borrowed, and it represents the bulk of your debt. When making payments, it’s essential to prioritize paying off the principal as it directly reduces the outstanding balance. By allocating a larger portion of your monthly payment towards the principal, you can expedite the repayment process and reduce the overall interest paid.
Interest
Interest is the cost of borrowing money, and it is calculated based on the remaining principal balance. While paying off the principal is important, neglecting the interest can result in increasing debt due to accruing interest charges. It’s crucial to allocate a portion of your monthly payment towards settling the interest to avoid falling into a debt spiral. By staying on top of the interest payments, you can prevent the outstanding balance from growing over time.
Fees And Charges
Aside from the principal and interest, there may be additional fees and charges associated with your loan. These can include origination fees, late payment penalties, or other administrative costs. While fees and charges may not make up a significant portion of your monthly payment, neglecting them can lead to additional penalties or even default on the loan. Therefore, it’s important to prioritize these payments to maintain a good financial standing.
Impact On Loan Repayment
Loan repayment is impacted by the order of payment in an amortization schedule. Generally, the principal and interest get paid first, followed by any additional fees or charges. It’s important to understand this order to effectively manage loan repayments.
Impact on Loan Repayment When it comes to loan repayment, understanding what gets paid first on an amortization schedule is crucial for effectively managing your financial commitments. This knowledge can help you develop cost-saving strategies and long-term financial planning to minimize interest payments and accelerate your path to debt freedom.Cost Saving Strategies
Implementing cost-saving strategies can have a significant impact on your loan repayment journey. By allocating additional funds towards the principal balance, you can effectively reduce the overall interest paid over the life of the loan. This approach enables you to decrease the loan term, saving you money in the long run.Long-term Financial Planning
Long-term financial planning plays a pivotal role in ensuring a secure financial future. By focusing on paying off high-interest debts first, such as credit cards or personal loans, you can free up more funds to allocate towards mortgage payments. This strategy can lead to substantial interest savings and help you become debt-free sooner. With careful consideration of what gets paid first on an amortization schedule, you can formulate effective cost-saving strategies and long-term financial plans, ultimately accelerating your journey to financial independence.
Credit: www.boe.ca.gov
Default And Foreclosure
In an amortization schedule, the order of priority for payment is predetermined, with the principal balance receiving payment first, followed by interest, taxes, and insurance. This ensures that the borrower meets their obligations in the event of default or foreclosure.
When it comes to an amortization schedule, default and foreclosure are key factors to consider. Default occurs when a borrower fails to make their mortgage payments according to the agreed terms. This can happen due to financial difficulties, job loss, or other unforeseen circumstances. Foreclosure, on the other hand, is the legal process by which a lender takes possession of a property to recover the outstanding balance. Understanding the consequences and legal implications of default and foreclosure is crucial for both borrowers and lenders.Consequences
Defaulting on mortgage payments can lead to a range of consequences. One significant consequence is the negative impact it has on your credit score. A default can cause your credit score to plummet, making it difficult to secure future loans or lines of credit. Additionally, a default can result in late fees and penalties, which can further worsen your financial situation. As a borrower, it’s important to be aware of and address any defaults promptly to mitigate these consequences.Legal Implications
Default and foreclosure also have legal implications that both borrowers and lenders should understand. When a borrower defaults on their mortgage, the lender may initiate legal proceedings to recover their investment. This can involve a foreclosure process, where the lender seeks to sell the property to recoup the outstanding debt. It is important to consult legal advice and understand your rights and responsibilities when facing default or foreclosure. In many jurisdictions, lenders are required to follow strict legal procedures when pursuing foreclosure. These procedures are designed to protect the rights of the borrower and ensure a fair process. Understanding the legal implications surrounding default and foreclosure can help borrowers navigate the complex legal landscape and potentially explore options to avoid foreclosure, such as loan modification or refinancing. In conclusion, default and foreclosure are significant aspects of a mortgage and the accompanying amortization schedule. They can have serious consequences for borrowers, including damage to their credit score and financial penalties. Additionally, default and foreclosure have legal implications that both borrowers and lenders must be aware of in order to protect their rights and make informed decisions. By understanding these aspects, borrowers can take proactive measures to address defaults and seek alternatives to foreclosure.Managing Priorities
When it comes to managing your finances, prioritizing your payments is crucial. Understanding what gets paid first on an amortization schedule can help you effectively manage your financial obligations and stay on top of your budget. In this section, we will explore two key aspects that will assist you in managing your priorities: effective payment strategies and budgeting techniques.
Effective Payment Strategies
Having a well-defined plan for making payments is the foundation of managing your finances successfully. By implementing effective payment strategies, you can ensure that you allocate your resources in the optimal manner. Here are a few strategies to consider:
- Pay the minimum due on all your debts to avoid late fees and penalties – this should be your top priority.
- Focus on high-interest debts first, as they can cost you more in the long run. By paying off these debts quickly, you can minimize your overall interest expenses.
- If you have multiple debts, consider the snowball or avalanche method. With the snowball method, you pay off the smallest debt first, gaining momentum. On the other hand, the avalanche method involves tackling the highest-interest debt first.
- Automating your payments can help you stay consistent and avoid missing due dates. Set up automatic payments through your bank or use online payment tools to streamline the process.
Budgeting Techniques
Creating and adhering to a budget allows you to better manage your finances and prioritize your payments. Here are some budgeting techniques to help you stay on track:
- Start by tracking your income and expenses to get a clear picture of your financial situation. This will help you identify areas where you can reduce spending.
- Allocate a specific amount for each category, such as housing, transportation, groceries, and debt payments, in your budget. Be realistic and ensure your expenses do not exceed your income.
- Consider adopting the envelope system, where you assign physical envelopes for different expense categories. This way, you have a tangible reminder of your budget limits and can avoid overspending.
- Regularly review your budget to make adjustments as needed. Life circumstances may change, requiring you to reallocate funds or reprioritize your expenses.
By implementing effective payment strategies and utilizing budgeting techniques, you can better manage your financial priorities and stay on top of your payments. Keeping a consistent approach and staying disciplined will set you on the path to financial stability and success.

Credit: medium.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Gets Paid First An An Amortization Schedule?
What Is An Amortization Schedule And How Does It Work?
An amortization schedule is a table that shows the breakdown of loan payments over time, including the interest and principal amounts. It helps borrowers understand how much they pay towards interest and how much goes towards paying off the loan balance.
Does The Interest Get Paid First On An Amortization Schedule?
Yes, when you make a payment on an amortization schedule, the interest portion of the payment is typically paid first. This is because lenders want to ensure that they receive the interest owed to them before any principal payments are made.
Can I Choose Which Debt Gets Paid First On An Amortization Schedule?
Typically, on an amortization schedule, the lender determines the allocation of payments towards interest and principal. However, some lenders may allow borrowers to specify how they want their payments applied, such as towards a specific debt account or reducing the loan principal.
It’s best to consult with your lender to understand their specific policies.
What Happens If I Make Extra Principal Payments On An Amortization Schedule?
If you make extra principal payments on an amortization schedule, it can help reduce the overall interest you pay and shorten the loan term. These additional payments go directly towards reducing the loan principal, allowing you to pay off the debt faster and potentially save money on interest charges.
Conclusion
Understanding the order of payment on an amortization schedule is crucial for financial health. Allocating funds to interest, then principal, aids in reducing long-term debt. Prioritizing these payments ensures a smooth repayment process, ultimately saving money over time. Implementing this knowledge can have a positive impact on personal finances.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is an amortization schedule and how does it work?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “An amortization schedule is a table that shows the breakdown of loan payments over time, including the interest and principal amounts. It helps borrowers understand how much they pay towards interest and how much goes towards paying off the loan balance.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Does the interest get paid first on an amortization schedule?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Yes, when you make a payment on an amortization schedule, the interest portion of the payment is typically paid first. This is because lenders want to ensure that they receive the interest owed to them before any principal payments are made.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Can I choose which debt gets paid first on an amortization schedule?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Typically, on an amortization schedule, the lender determines the allocation of payments towards interest and principal. However, some lenders may allow borrowers to specify how they want their payments applied, such as towards a specific debt account or reducing the loan principal. It’s best to consult with your lender to understand their specific policies.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What happens if I make extra principal payments on an amortization schedule?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “If you make extra principal payments on an amortization schedule, it can help reduce the overall interest you pay and shorten the loan term. These additional payments go directly towards reducing the loan principal, allowing you to pay off the debt faster and potentially save money on interest charges.” } } ] }