Pik Power: Understanding How Pik Works in Preferred Equity
PIK (Payment-in-Kind) works in preferred equity by allowing investors to receive interest payments in the form of additional shares instead of cash. These additional shares increase the investor’s ownership in the company.
This structure provides companies with the benefit of conserving cash flow while still honoring their obligations to investors. Preferred equity, a type of financing instrument, plays a crucial role in businesses seeking capital. It offers investors a unique advantage by granting them prioritized claim over common equity holders in case of liquidation events.
One interesting feature within preferred equity is the use of Payment-in-Kind (PIK) provisions. PIK enables issuers to fulfill their interest payment obligations by issuing additional shares to investors rather than providing cash payments. This mechanism helps companies conserve cash while simultaneously compensating investors. We will delve into how PIK works, understand its benefits for both issuers and investors, and explore its potential implications in the realm of preferred equity. So, let’s dive in and uncover the intricacies of PIK in preferred equity.

Credit: www.wallstreetprep.com
The Concept Of Pik Power
The concept of Pik power is an important aspect to understand when it comes to preferred equity. Pik power refers to the payment-in-kind feature that allows a company to pay interest or dividends by issuing additional preferred equity instead of cash. This unique feature provides flexibility to companies and investors alike, allowing for creative financing solutions. In this section, we will explore the definition of Pik power and its application in preferred equity.
Definition Of Pik Power
Pik power, short for payment-in-kind power, is a financial tool that enables companies to defer cash payments by issuing additional preferred equity instead. This means that interest or dividends owed to preferred equity investors can be paid with additional preferred equity shares, offering a non-cash alternative. It is a mutually agreed arrangement that provides flexibility for both the company and the investors.
Application In Preferred Equity
Pik power finds its application primarily in preferred equity, which is a form of equity that falls between debt and common equity. Preferred equity holders receive preferential treatment in terms of dividend payments, distribution of assets during liquidation, and a higher claim on company assets over common equity holders. The use of Pik power in preferred equity allows companies to provide the agreed-upon returns to investors without immediate cash outflows.
By utilizing Pik power, companies can navigate challenging financial situations where they may not have sufficient cash flow to meet their payment obligations. This tool can help them manage their liquidity while maintaining stability and financial health. Additionally, it can be an attractive option for investors who are willing to defer their cash payments and instead obtain further ownership in the company through additional preferred equity.
Benefits Of Pik Power
Pik Power offers beneficial methods for preferred equity financing. By leveraging its unique structure, Pik can provide more flexibility and lower costs for real estate developers. The distinct features of Pik power enable developers to maximize their returns and optimize their capital structure for long-term success.
Enhanced Returns For Investors
Investing in preferred equity with a Pik (Payment-in-Kind) feature can provide enhanced returns for investors. This means that instead of receiving regular cash payments, investors have the option to receive additional shares or equity instead.
A Pik structure allows investors to participate in the growth of the company, as the additional equity received can appreciate in value over time. This can potentially result in higher overall returns compared to traditional payment structures.
By choosing the Pik option, investors can benefit from the potential capital appreciation of the company they have invested in. This feature can be particularly appealing for investors looking for higher upside potential and who are willing to forego immediate cash payments.
Flexibility In Payment Structures
Pik power offers investors flexibility in payment structures by providing alternative methods of compensation. Instead of relying solely on cash payments, investors have the option to receive shares or equity in the company.
This flexibility can be beneficial for both the investor and the company. For the investor, it provides an opportunity to diversify their investment portfolio and potentially capture additional value through equity ownership.
For the company, the Pik structure offers greater flexibility in managing its cash flow. By providing the option to pay with additional equity, the company can conserve cash for other operational needs or growth initiatives. This can be particularly advantageous for companies in industries where cash flow can be variable or where the ability to defer cash payments is beneficial.
Furthermore, the Pik structure can also be used strategically to incentivize investors and align their interests with the long-term goals of the company. By offering the potential for increased equity ownership, the company can encourage investor loyalty and commitment to the company’s success.
Risks And Considerations
When considering preferred equity through PiK (Payment in Kind), it’s crucial to be aware of the associated risks and considerations. Understanding the potential impacts on a company’s financial health and the potential disadvantages for investors is essential for making informed decisions in this type of investment.
Impact On Company’s Financial Health
The utilization of PiK in preferred equity can have a significant impact on a company’s financial health. When a company elects to issue PiK preferred equity, it doesn’t make regular cash interest payments. Instead, the interest is added to the principal amount of the investment. This can lead to a growth in the company’s debt burden over time. While this may provide short-term relief by conserving cash, in the long run, it could strain the company’s financial position and limit its ability to pursue growth opportunities.
Potential Disadvantages For Investors
- Lack of regular income: Investing in PiK preferred equity means that investors may not receive regular income in the form of cash interest payments.
- Increased risk: The growth of the company’s debt burden due to the accumulation of unpaid interest could elevate the risk for investors, particularly in the event of financial distress or default.
- Diminished liquidity: PiK preferred equity may lack the liquidity of other types of investments, making it challenging for investors to access their capital when needed.

Credit: www.wallstreetprep.com
Regulatory And Legal Aspects
Preferred equity is regulated by various legal aspects, ensuring proper functioning of PIK (payment-in-kind) instruments. This entails compliance with regulatory frameworks, legal documentation, and investor protection laws, enabling companies to use PIK to fund growth and meet financial objectives.
Compliance With Securities Law
When it comes to preferred equity and the functioning of PIK (payment-in-kind), regulatory and legal aspects play a crucial role. Compliance with securities law is a key consideration for companies utilizing PIK in their preferred equity structure. Adhering to securities law ensures that companies are operating within the legal boundaries and preventing any potential legal risks. This includes obtaining necessary approvals and licenses to issue preferred equity and incorporating necessary disclosures for investors. Companies must comply with regulations set by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States or other relevant regulatory bodies in different jurisdictions. This involves ensuring that the issuance of preferred equity aligns with the rules and regulations applicable to securities offerings. In addition to complying with securities law, companies must also consider any regulations specific to the industry they operate in. These regulations may vary depending on the sector, such as banking, technology, or healthcare. Compliance with securities law not only protects the company from legal consequences but also provides investors with a sense of confidence and trust in the organization’s financial operations.Impact On Corporate Governance
The implementation of PIK in preferred equity can have a significant impact on corporate governance within a company. Corporate governance refers to the structure, policies, and processes that oversee the decision-making and accountability of a company’s management. By utilizing PIK in preferred equity, companies may alter their capital structure, leading to potential changes in the power dynamics and decision-making processes within the organization. This can further impact the roles and responsibilities of the board of directors and executive management. The use of PIK in preferred equity can provide management with more flexibility to make strategic decisions. It allows companies to defer cash payments, use funds for other purposes, or invest in growth opportunities. However, this also means that investors may have limited or no immediate access to cash dividends. As a result, it becomes essential for companies to ensure transparency and clear communication with investors regarding the impact of PIK on corporate governance. This includes providing detailed information about any changes in decision-making processes and the potential implications for shareholders. In addition, companies need to establish appropriate reporting mechanisms and accountability frameworks to maintain good corporate governance practices. This involves disclosing relevant information to shareholders and regularly evaluating the effectiveness of the governance structure. By maintaining a strong corporate governance framework and addressing the impact of PIK, companies can foster trust and confidence among shareholders, ensuring the smooth functioning of the preferred equity structure.Comparison With Other Financing Mechanisms
When it comes to financing options, preferred equity through Pik financing offers distinct advantages that set it apart from other mechanisms, such as common equity and traditional debt. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses seeking the optimal financing solution.
Contrast With Common Equity
Unlike common equity, which grants investors voting rights and ownership shares in a company, preferred equity provides investors with a fixed claim on assets and income. This means that preferred equity holders have priority in receiving dividends and liquidation proceeds, making it an attractive option for investors who desire regular income and downside protection.
Comparatively, common equity investors assume higher risk and rely on the company’s growth for returns. They benefit from voting rights, allowing them to influence key decisions, but their returns are not guaranteed and depend on the performance of the business. Preferred equity, on the other hand, offers more stability and predictable returns.
Distinctions From Traditional Debt
Pik financing also differs significantly from traditional debt. When a company borrows from traditional lenders, it incurs an obligation to repay the debt along with interest. Failure to meet repayment obligations can result in severe consequences, such as foreclosure or bankruptcy. In contrast, preferred equity functions more like an investment instrument, where investors participate in the company’s growth and success.
Unlike traditional debt, preferred equity does not impose strict repayment terms. Instead, investors receive dividends or another predetermined financial arrangement based on the company’s performance. This flexibility in the payment structure makes preferred equity a viable financing option for businesses that prefer to avoid additional debt burdens or have uncertain cash flows.
However, it is important to note that preferred equity comes with its own set of risks. While it offers a lower level of risk compared to common equity, investors still face the possibility of loss if the company experiences financial difficulties or fails to generate enough profits. It is essential for businesses considering preferred equity to carefully evaluate their financial situation and the potential impact on their ownership structure.
In conclusion, Pik financing in the form of preferred equity provides businesses with an alternative financing mechanism that has clear contrasts from common equity and traditional debt. By understanding these distinctions, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their specific financing needs and objectives.
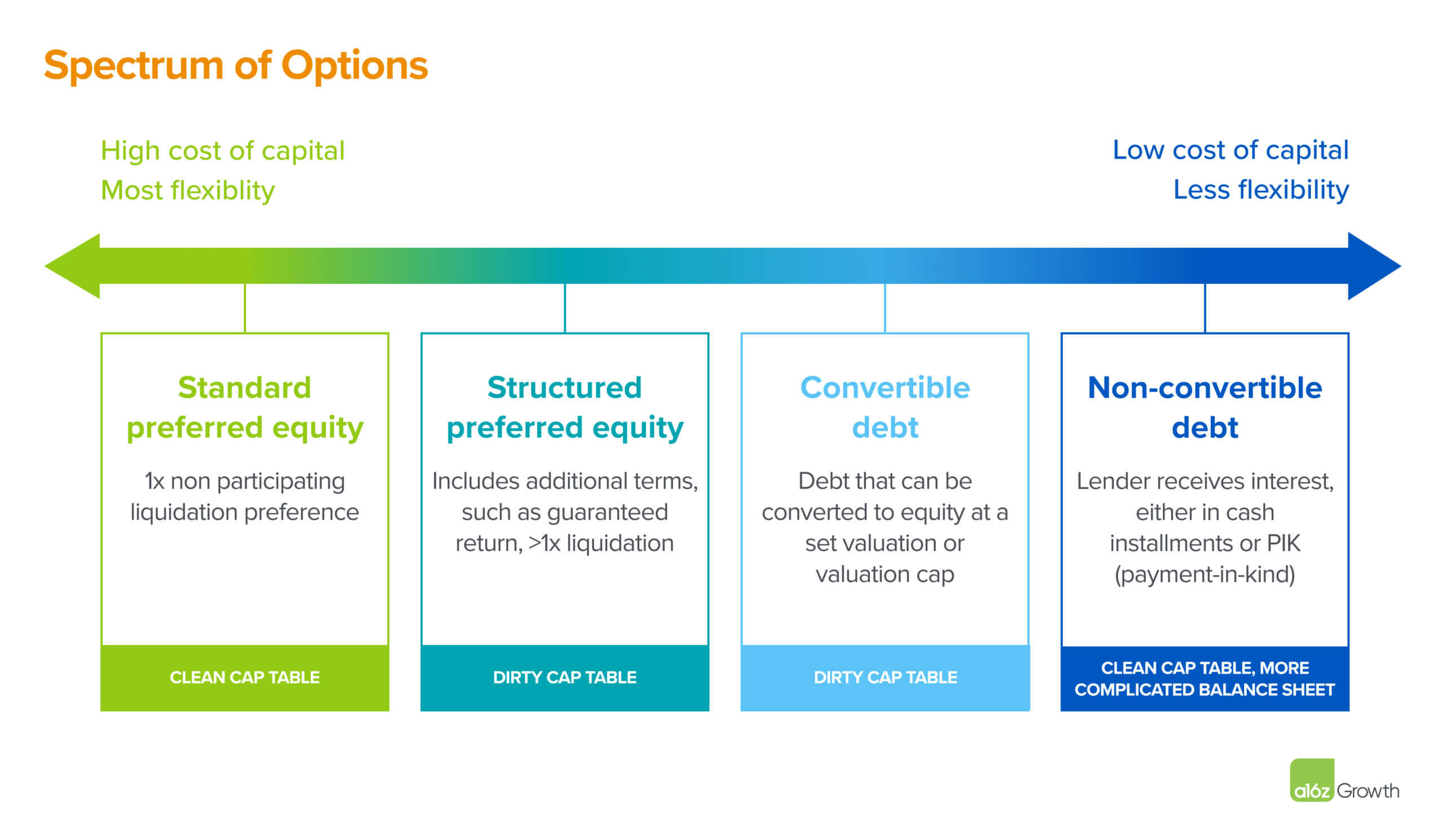
Credit: a16z.com
Frequently Asked Questions For How Does Pik Work In Preferred Equity?
What Is Preferred Equity In Real Estate?
Preferred equity in real estate refers to a type of investment where investors receive a fixed return before common equity holders. It offers a hybrid investment structure that combines elements of debt and equity, providing investors with downside protection and potential upside.
This type of equity is often used in commercial real estate projects to help fund development or acquisition.
How Does Pik Work In Preferred Equity?
PIK, or pay-in-kind, is a feature in preferred equity that allows investors to receive their returns in the form of additional equity rather than cash. This means that instead of receiving periodic cash payments, investors can choose to accumulate more ownership in the property.
PIK increases an investor’s potential upside while deferring cash payments until a later date.
What Are The Benefits Of Preferred Equity With Pik?
Preferred equity with PIK offers several benefits. It provides investors with the potential for higher returns through the accumulation of additional equity. It also allows investors to defer cash payments and reinvest the returns back into the project, increasing their ownership stake over time.
This structure can be attractive for both investors seeking long-term capital appreciation and developers looking for flexible financing options.
What Are The Risks Associated With Preferred Equity?
Like any investment, preferred equity carries risks. Investors may face the risk of not receiving expected cash returns if the project underperforms. They may also face liquidity risk, as their returns are often tied to the property’s future cash flows or a sale event.
Additionally, preferred equity investors may have limited control over the project’s management decisions, relying on the operator’s expertise and decision-making.
Conclusion
Understanding how PIK works in preferred equity can provide valuable insight for investors. By offering the option to receive payment in-kind, PIK financing offers flexibility and can be an advantageous tool for companies seeking capital. This unique structure allows for creative financial solutions in a dynamic market environment.
Understanding PIK and its potential impact is essential for informed decision making.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is preferred equity in real estate?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Preferred equity in real estate refers to a type of investment where investors receive a fixed return before common equity holders. It offers a hybrid investment structure that combines elements of debt and equity, providing investors with downside protection and potential upside. This type of equity is often used in commercial real estate projects to help fund development or acquisition.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does Pik work in preferred equity?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “PIK, or pay-in-kind, is a feature in preferred equity that allows investors to receive their returns in the form of additional equity rather than cash. This means that instead of receiving periodic cash payments, investors can choose to accumulate more ownership in the property. PIK increases an investor’s potential upside while deferring cash payments until a later date.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the benefits of preferred equity with Pik?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Preferred equity with PIK offers several benefits. It provides investors with the potential for higher returns through the accumulation of additional equity. It also allows investors to defer cash payments and reinvest the returns back into the project, increasing their ownership stake over time. This structure can be attractive for both investors seeking long-term capital appreciation and developers looking for flexible financing options.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What are the risks associated with preferred equity?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Like any investment, preferred equity carries risks. Investors may face the risk of not receiving expected cash returns if the project underperforms. They may also face liquidity risk, as their returns are often tied to the property’s future cash flows or a sale event. Additionally, preferred equity investors may have limited control over the project’s management decisions, relying on the operator’s expertise and decision-making.” } } ] }