How Do You Amortize a Loan Example? Discover the Most Effective Method
To amortize a loan, calculate the monthly payment and allocate a portion to interest and the remainder to principal. Here’s an example.
Amortizing a loan involves spreading out the repayment of a loan over a specific period with regular installments. This method ensures that both the principal amount and the interest are gradually paid off. By knowing how to amortize a loan, borrowers can better understand their repayment schedule and plan their finances accordingly.
We will provide an example of how to amortize a loan to illustrate the process step by step. Whether you are taking out a mortgage loan or repaying a car loan, understanding how to amortize a loan can help you stay on top of your payments and manage your debt effectively.

Credit: www.spreadsheet.com
Understanding Amortization
Amortization Definition
Before we dive into the example of how to amortize a loan, let’s understand what amortization means. Amortization refers to the process of gradually paying off a loan over a predefined period. This method ensures that the principal amount, along with the interest, is paid in equal installments throughout the loan tenure. By following an amortization schedule, borrowers can track their progress and stay on top of their loan payments.
Importance Of Understanding Amortization
It is crucial to comprehend the concept of amortization, as it helps borrowers make informed financial decisions. Here are a few reasons why understanding amortization is important:
- Budgeting: By understanding how amortization works, borrowers can plan their monthly budgets accordingly. They can anticipate the amount they need to set aside each month to fulfill their loan obligations without straining their finances.
- Interest Savings: Through amortization, borrowers can save on interest payments over time. By paying off more principal in the earlier stages of the loan, they reduce the outstanding balance and subsequently the interest charged. This knowledge empowers borrowers to make extra payments and potentially shorten the loan tenure.
- Transparency: Amortization schedules provide complete transparency about the loan terms and repayment process. Borrowers can clearly see how their payment affects the principal and interest portions, enabling them to track progress and remain aware of their financial obligations.
Now that we understand the significance of amortization, let’s explore an example to comprehend the practical implementation of this concept.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amortized_loan.asp-final-23646fe3883e4f87902df8207a750e0a.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Amortization Schedule
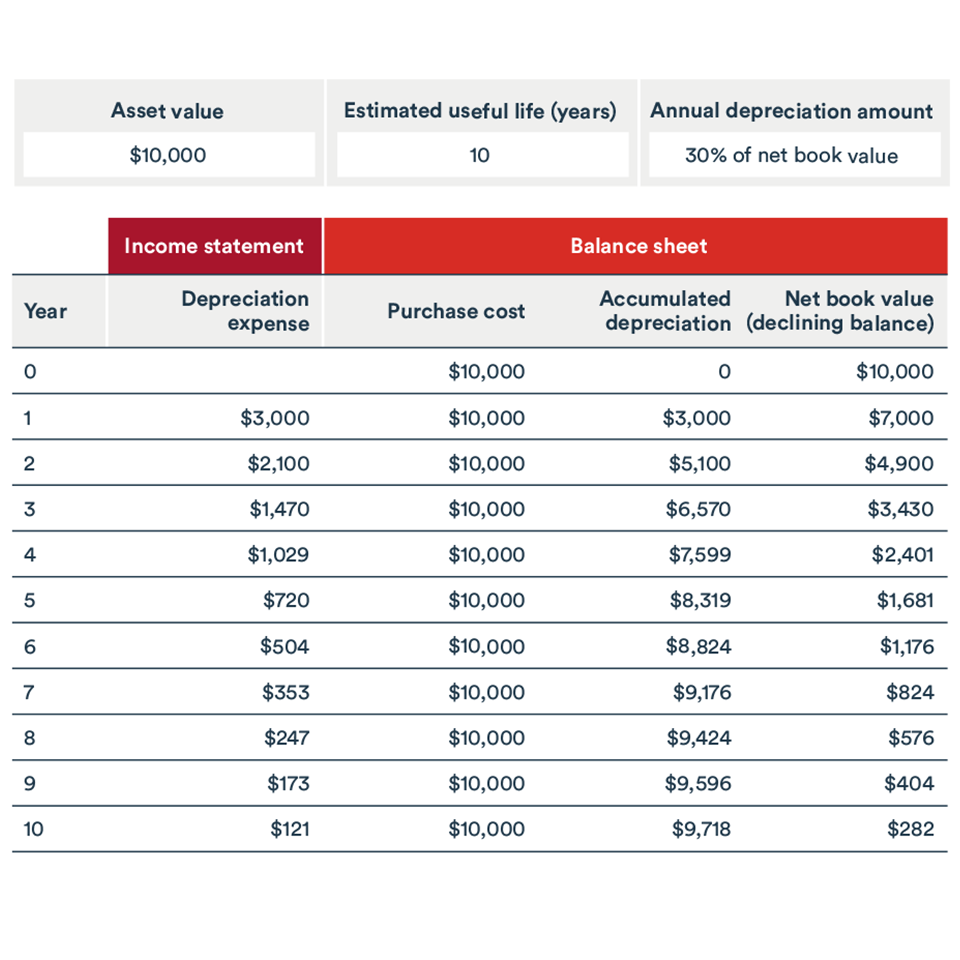
To amortize a loan, use an amortization schedule to track how each payment is split between principal and interest. For example, with a $10,000 loan at 5% interest over 5 years, the schedule would show monthly payments and the decreasing loan balance as principal is paid off along with interest.
Components Of An Amortization Schedule
An amortization schedule is a useful tool that helps you understand how your loan will be repaid over time. It provides a detailed breakdown of every payment, showing how much will go towards principal and how much towards interest. Understanding the components of an amortization schedule can greatly assist you in managing your loan.Calculating Monthly Payments
Calculating monthly payments for a loan requires a few key pieces of information. These include the loan amount, interest rate, and the loan term. By plugging these values into a formula, you can determine what your monthly payment will be. Let’s take a look at an example to make it easier to understand. Suppose you borrow $10,000 at an interest rate of 5% for a term of 5 years. To calculate the monthly payment, you can use the following formula: Monthly Payment = P × (r × (1 + r)^n) / ((1 + r)^n – 1) P is the principal amount, r is the monthly interest rate (annual rate divided by 12), and n is the number of monthly payments (total months in the loan term). In this example, the formula would be: Monthly Payment = $10,000 × (0.05 / 12 × (1 + 0.05 / 12)^60) / ((1 + 0.05 / 12)^60 – 1) This calculation would give you the exact amount you need to pay each month. Now that you understand how to calculate your monthly payments, let’s dive into the concept of an amortization schedule. An amortization schedule provides a month-by-month breakdown of your loan repayment, showing the changes in principal and interest over time. The schedule typically includes the following information:- Month and Year: Each row in the schedule represents a specific month and year of the loan term.
- Beginning Balance: This is the outstanding loan balance at the start of each month.
- Payment: The monthly payment you calculated earlier is listed here.
- Principal: The amount of your payment that goes towards reducing the loan balance.
- Interest: The portion of your payment that covers the interest on the remaining balance.
- Ending Balance: The remaining loan balance after deducting the principal payment.
Amortization Methods
When it comes to amortizing a loan, there are different methods that can be employed to distribute the repayment of a loan over a specified period. These methods are essential in understanding how the interest and principal components change over time. In this blog post, we will delve into the two common amortization methods: straight-line amortization and effective interest rate method.
Straight-line Amortization
This method involves spreading the total interest expense evenly over the loan term and allocating a fixed portion of the principal to each period. It is widely used for simple consumer loans where the interest and principal payments remain constant throughout the loan term.
Effective Interest Rate Method
The effective interest rate method is commonly utilized for more complex loans, such as mortgages and business loans. Under this method, a constant periodic interest rate is applied to the remaining balance of the loan, resulting in varying interest and principal payments over time.
Amortization Example
Looking for an example of how to amortize a loan? Check out this brief and easy-to-understand explanation that outlines the step-by-step process of loan amortization. With clear and concise examples, you’ll gain a better understanding of how to calculate the payments and allocate them towards both the principal and interest over time.
Step-by-step Loan Amortization Example
In this section, we will walk you through a step-by-step loan amortization example, which will help you understand the process better. Let’s assume you have taken out a $10,000 loan with an annual interest rate of 5% and a term of 5 years. We will calculate the monthly payments and analyze the amortization results.
Analyzing The Amortization Results
Now that we have calculated the monthly payments and created an amortization schedule, let’s analyze the results:
- Principal Payment: The portion of each monthly payment that goes towards reducing the loan amount.
- Interest Payment: The portion of each monthly payment that goes towards paying the interest on the loan.
- Total Payment: The sum of the principal and interest payments for each month.
- Outstanding Balance: The remaining loan balance after each monthly payment has been made.
By analyzing the amortization results, you can get a clear picture of how your loan is being repaid over time. This information can help you make informed financial decisions and plan your budget accordingly.
| Month | Principal Payment | Interest Payment | Total Payment | Outstanding Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $166.02 | $41.67 | $207.69 | $9,833.98 |
| 2 | $167.34 | $40.35 | $207.69 | $9,666.64 |
| 3 | $168.67 | $39.02 | $207.69 | $9,497.97 |
| 4 | $170.01 | $37.68 | $207.69 | $9,327.96 |
| 5 | $171.36 | $36.33 | $207.69 | $9,156.60 |
In summary, understanding how to amortize a loan is crucial in managing your finances effectively. By analyzing the step-by-step loan amortization example and reviewing the results, you can gain insights into your loan repayment journey. This knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions and stay on top of your financial obligations.
Benefits Of Amortizing A Loan
Amortizing a loan allows you to spread out your payments over time, making it easier to budget and manage your finances. For example, instead of paying a lump sum, you can make regular payments that gradually reduce both the principal and interest owed.
This method offers several benefits, including lower monthly payments and the ability to build equity in the asset being financed.
Amortizing a loan comes with several advantages that can make it a smart financial decision. Understanding these benefits can help you navigate the loan repayment process with confidence. Let’s explore two key benefits of amortizing a loan: building equity and lower interest costs.
Building Equity
Amortizing a loan allows you to build equity in the asset or property that you are financing. Equity represents the portion of the property that you own outright, without any debt attached to it. As you make monthly payments towards the loan principal, the equity in your property increases over time. This is especially beneficial if you plan to sell the property in the future or use it as collateral for other financial needs.
For example, if you have a mortgage loan for a house, each monthly payment reduces the outstanding balance of your loan and increases your ownership stake in the property. This can be a crucial factor when it comes to building long-term wealth and financial stability.
Lower Interest Costs
Another advantage of amortizing a loan is the potential for lower interest costs compared to other loan repayment methods. With an amortizing loan, your payments are structured so that a portion goes towards the principal balance and another portion covers the interest charges.
Over time, as you continue to make payments, the principal balance decreases, which in turn reduces the amount of interest that accrues on the loan. This means that as the loan matures, a larger portion of your payments goes towards paying down the principal, resulting in lower overall interest costs throughout the life of the loan.
Let’s demonstrate this with a simple example: If you have a $100,000 loan with a 6% interest rate, your monthly payment may be a fixed amount of $600. In the beginning, a larger portion of your payment goes towards interest, while a smaller portion is allocated to the principal balance. However, as time goes on, the ratio shifts, and more of your payment is applied to reducing the principal debt.
By amortizing the loan, you have the potential to save a significant amount of money in interest charges over the course of repayment. With lower interest costs, you are able to allocate more of your financial resources towards other important goals, such as savings, investments, or paying off additional debts.
Conclusion
Amortizing a loan provides benefits that can help you build equity and save on interest costs over time. By understanding these advantages, you can make informed decisions about your financial future and choose the loan repayment method that aligns with your goals. So, now that you grasp the benefits of amortizing a loan, you are well-equipped to plan your financial journey accordingly.
Credit: www.bdc.ca
Frequently Asked Questions Of How Do You Amortize A Loan Example?
How Do You Amortize A Loan Example?
Amortizing a loan involves making regular payments towards both the principal amount and the interest. An example would be paying a fixed amount each month for a set period, gradually reducing the loan balance. This method ensures that the loan is fully paid off by the end of the term.
It is a popular choice for mortgages and car loans.
What Is The Purpose Of Loan Amortization?
The purpose of loan amortization is to evenly distribute the payments over the loan term, resulting in a gradual reduction of the outstanding balance. This allows borrowers to budget their payments and ensures that the loan will be fully paid off by the end of the term.
Amortization also helps in calculating the interest portion and principal portion of each payment.
How Does Loan Amortization Benefit Borrowers?
Loan amortization provides several benefits to borrowers. Firstly, it allows for budgeting as the payments are fixed and predictable. Secondly, it ensures that the loan will be fully paid off by the end of the term. Additionally, amortization helps in building equity in an asset such as a house or a car.
Lastly, it helps in calculating the total interest paid over the loan term.
Are There Any Disadvantages To Loan Amortization?
While loan amortization has its benefits, it also has a few disadvantages. One drawback is that the initial payments are primarily allocated towards interest, resulting in a slower reduction of the principal balance. Additionally, if interest rates decrease, borrowers might miss out on potential savings as they are locked into a fixed payment schedule.
It is important to weigh these factors when considering loan options.
Conclusion
Understanding how to amortize a loan is crucial for managing your finances wisely. By spreading out the loan over a period of time, you can minimize the impact on your monthly budget and better plan for future expenses. Take the time to analyze your loan terms and develop a structured repayment strategy.
With a clear understanding of loan amortization, you can make informed financial decisions and achieve your long-term goals.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How do you amortize a loan example?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Amortizing a loan involves making regular payments towards both the principal amount and the interest. An example would be paying a fixed amount each month for a set period, gradually reducing the loan balance. This method ensures that the loan is fully paid off by the end of the term. It is a popular choice for mortgages and car loans.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the purpose of loan amortization?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The purpose of loan amortization is to evenly distribute the payments over the loan term, resulting in a gradual reduction of the outstanding balance. This allows borrowers to budget their payments and ensures that the loan will be fully paid off by the end of the term. Amortization also helps in calculating the interest portion and principal portion of each payment.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does loan amortization benefit borrowers?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Loan amortization provides several benefits to borrowers. Firstly, it allows for budgeting as the payments are fixed and predictable. Secondly, it ensures that the loan will be fully paid off by the end of the term. Additionally, amortization helps in building equity in an asset such as a house or a car. Lastly, it helps in calculating the total interest paid over the loan term.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Are there any disadvantages to loan amortization?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “While loan amortization has its benefits, it also has a few disadvantages. One drawback is that the initial payments are primarily allocated towards interest, resulting in a slower reduction of the principal balance. Additionally, if interest rates decrease, borrowers might miss out on potential savings as they are locked into a fixed payment schedule. It is important to weigh these factors when considering loan options.” } } ] }