How Do I Calculate Amortization? Master the Art of Debt Repayment!
To calculate amortization, divide the loan amount by the loan term and multiply by the interest rate. Amortization is a crucial aspect of understanding and managing loans.
By calculating amortization, you can determine how much of each loan payment goes towards principal and interest. This helps you plan your repayment strategy, budget effectively, and make informed financial decisions. To calculate amortization, you need to divide the loan amount by the loan term and then multiply it by the interest rate.
This simple calculation allows you to visualize how your loan will be paid off over time, enabling you to plan your finances accordingly. Whether you’re taking out a mortgage, car loan, or any other type of loan, understanding amortization is essential for managing your debt responsibly.
The Basics Of Amortization
In the world of finance and loans, amortization is a crucial concept to understand. Whether you’re looking to purchase a new home or start a business, knowing how to calculate amortization is essential. In this blog post, we will break down the basics of amortization, including what it is and how it works.
What Is Amortization?
Amortization refers to the process of gradually paying off a debt or loan over time through regular installments. It involves breaking down the total borrowed amount into smaller, regular payments that include both principal and interest. These payments are typically made on a monthly basis, allowing borrowers to gradually reduce their debt until it is fully paid off.
Understanding Loan Amortization
When it comes to understanding loan amortization, it’s important to know the key components involved. These include the principal amount, interest rate, loan term, and payment frequency. The principal amount refers to the total borrowed sum, while the interest rate determines how much interest will be charged on the remaining balance.
Loan term, on the other hand, refers to the length of time the borrower has agreed to repay the loan. This can vary depending on the type of loan and the agreement between the borrower and lender. Finally, payment frequency refers to how often the borrower needs to make payments, whether it’s monthly, quarterly, or annually.
To calculate the amortization of a loan, you can use a formula or an online amortization calculator. The formula involves plugging in the loan details, such as the principal amount, interest rate, and loan term, to determine the monthly payment amount. This payment is then applied towards both the principal and the interest, gradually reducing the debt over time.
| Key Loan Details | |
|---|---|
| Principal Amount | $XXX,XXX |
| Interest Rate | X% |
| Loan Term | X years |
Once you have calculated the monthly payment amount, you can create an amortization schedule. This schedule displays how each payment is allocated towards the principal and interest, as well as the remaining balance after each payment. It helps borrowers visualize their progress and understand how their payments contribute to reducing the debt over time.
Understanding how to calculate amortization is essential for anyone looking to borrow money or manage their existing debts. By familiarizing yourself with the basics of amortization, you’ll be better equipped to make informed financial decisions and effectively plan for the future.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/interestcoverageratio-f7e7cdf96d4b4063a63d258ff5d775a8.jpg)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Key Components Of Amortization
The key components of amortization are principal and interest, and the amortization schedule. Understanding these components is crucial for calculating amortization accurately and efficiently. Let’s dive into each of these components in detail.
Principal And Interest
When you take out a loan, the principal is the initial amount of money you borrow. It is the total amount that you will need to repay. The interest, on the other hand, is the additional amount you pay to the lender for the privilege of borrowing the money. It is usually expressed as a percentage of the principal and is a way for the lender to earn profit from the loan.
Calculating the principal and interest is essential for determining your monthly payments and tracking your progress in paying off the loan. By understanding how the principal and interest are calculated, you can make informed decisions when managing your finances.
Amortization Schedule
The amortization schedule lays out the details of your loan repayment plan. It provides a clear overview of your monthly payments, the allocation of each payment towards the principal and interest, and the remaining balance after each payment.
An amortization schedule typically includes the following information:
- The date of each payment
- The total payment amount
- The amount allotted to interest
- The amount applied to the principal
- The remaining balance after each payment
This schedule helps you visualize how your loan balance decreases over time and how much of each payment goes towards paying off the principal. It can also be useful for planning your budget and understanding the impact of additional payments or changes in interest rates.
By referring to the amortization schedule, you can monitor your progress in repaying the loan and determine how much interest you will ultimately pay. This information can empower you to make financial decisions that align with your goals and optimize your loan repayment strategy.
Methods Of Amortization Calculation
When it comes to calculating amortization, there are several methods that can be used to determine how much of a loan payment goes towards the principal balance and how much goes towards the interest. Understanding these methods is crucial for individuals and businesses alike.
Straight-line Method
The straight-line method for calculating amortization is a simple and straightforward approach. It involves dividing the total cost of an asset (or the principal amount of a loan) by the number of periods in the loan term. This results in equal amortization amounts for each period, making it easy to budget and plan for repayments.
Effective Interest Rate Method
On the other hand, the effective interest rate method takes into account the changing value of the loan balance over time. By applying a constant interest rate to the remaining balance each period, the interest expense decreases while the principal repayment increases, providing a more accurate representation of the loan’s financial impact.

Credit: fastercapital.com
Amortization Calculation In Action
Making financial decisions requires a solid understanding of how amortization works. Whether you’re calculating the amortization schedule for a mortgage or a loan, the process remains the same. Let’s explore two different scenarios below that illustrate how amortization calculations can be put into action.
Using Excel For Amortization
If you’re comfortable with spreadsheets and want a quick and easy way to calculate amortization, Excel can be a powerful tool. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Create a new Excel spreadsheet and label the first column “Payment Number.”
- In the second column, label it “Beginning Balance.”
- Label the third column “Payment.”
- Next, label the fourth column as “Interest Paid.”
- In the fifth column, label it “Principal Repaid.”
- Label the sixth column “Ending Balance.”
- Enter the necessary information of your loan or mortgage in the appropriate cells.
- Using the correct formulas, calculate the values for each column in subsequent rows.
- Drag the formulas down to the remaining rows to automatically populate the values.
- You now have your amortization schedule!
Case Study: Calculating Amortization For A Mortgage
Let’s look at a real-life example of calculating amortization for a mortgage. Assume you have a $200,000 mortgage with an interest rate of 4.5% and a loan term of 30 years:
| Payment Number | Beginning Balance | Payment | Interest Paid | Principal Repaid | Ending Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $200,000 | $1,013.37 | $750 | $263.37 | $199,736.63 |
| 2 | $199,736.63 | $1,013.37 | $748.48 | $264.88 | $199,471.75 |
| 3 | $199,471.75 | $1,013.37 | $746.96 | $266.41 | $199,205.34 |
| 4 | $199,205.34 | $1,013.37 | $745.44 | $267.93 | $198,937.40 |
| 5 | $198,937.40 | $1,013.37 | $743.92 | $269.45 | $198,667.95 |
This table represents the first five payments and how they contribute to the mortgage amortization. As the payments progress, a larger portion goes towards reducing the principal balance, resulting in a lower outstanding balance. This helps you visualize the gradual decrease in your mortgage debt over time.
Maximizing The Benefits Of Amortization
Maximize the Benefits of Amortization Accelerating Debt RepaymentAccelerating Debt Repayment
One tangible advantage of amortization is the ability to accelerate debt repayment. By making extra payments towards your loan principal, you effectively reduce the overall interest paid over the loan term. This can help you pay off your debt faster and save thousands of dollars in interest. The key is to allocate any additional funds you have towards your loan principal, rather than solely making the minimum required payments.
- Make extra payments towards your loan principal to reduce overall interest.
- Pay off your debt faster and save thousands in interest.
Utilizing Amortization For Financial Planning
Amortization is not only a tool to calculate your loan payments; it can also be useful for financial planning purposes. By understanding the specific details of your loan, such as the repayment schedule and interest rates, you gain valuable insights into your future financial obligations. This allows you to plan your expenses, savings, and investments accordingly, ensuring you’re on track to meet your financial goals.
| Financial Planning Benefits of Amortization |
|---|
| Gain insights into your future financial obligations. |
| Plan your expenses, savings, and investments with accuracy. |
| Stay on track to meet your financial goals and objectives. |
Overall, amortization is a powerful financial tool that should not be overlooked. By accelerating debt repayment and utilizing amortization for financial planning, you can maximize the benefits of this method. Take control of your finances today and make informed decisions based on a solid understanding of amortization.
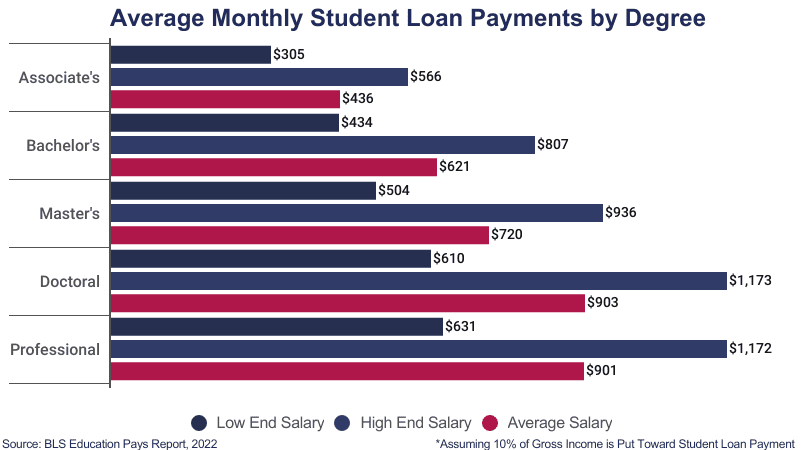
Credit: educationdata.org
Frequently Asked Questions On How Do I Calculate Amortization?
How Does Amortization Work?
Amortization is a method used to pay off a loan over time, reducing both the principal amount and the interest. Each payment is divided into portions that go toward the principal and the interest. As you make regular payments, the principal balance decreases, resulting in lower interest charges over time.
Why Is Amortization Important?
Amortization is essential because it allows borrowers to spread their loan payments over a longer period. This makes repayment more manageable and affordable. It also helps to allocate a larger portion of early payments towards interest, gradually shifting the focus towards the principal balance.
Understanding and managing amortization can help borrowers save money and pay off their loans more efficiently.
How Can I Calculate Amortization?
To calculate amortization, you’ll need to know the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. Use an amortization calculator or formula to determine your monthly payment, the portion allocated to interest, and the portion applied to the principal. By inputting different variables, you can tailor your calculation to match the specific details of your loan.
What Factors Affect The Amortization Process?
Several factors can impact the amortization process. The loan amount and interest rate are significant, as higher balances or rates increase the monthly payment and the total interest paid over the loan term. The loan term also plays a role, as longer terms result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs.
Additionally, making extra payments or refinancing can alter the amortization schedule.
Conclusion
Understanding amortization is crucial for making informed financial decisions. By utilizing the appropriate formula and tools, you can accurately compute the cost of loans and investments. Ultimately, this knowledge empowers you to manage your finances with confidence and clarity. As you expand your understanding of amortization, you can take control of your financial future.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does amortization work?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Amortization is a method used to pay off a loan over time, reducing both the principal amount and the interest. Each payment is divided into portions that go toward the principal and the interest. As you make regular payments, the principal balance decreases, resulting in lower interest charges over time.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Why is amortization important?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Amortization is essential because it allows borrowers to spread their loan payments over a longer period. This makes repayment more manageable and affordable. It also helps to allocate a larger portion of early payments towards interest, gradually shifting the focus towards the principal balance. Understanding and managing amortization can help borrowers save money and pay off their loans more efficiently.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How can I calculate amortization?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “To calculate amortization, you’ll need to know the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term. Use an amortization calculator or formula to determine your monthly payment, the portion allocated to interest, and the portion applied to the principal. By inputting different variables, you can tailor your calculation to match the specific details of your loan.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What factors affect the amortization process?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Several factors can impact the amortization process. The loan amount and interest rate are significant, as higher balances or rates increase the monthly payment and the total interest paid over the loan term. The loan term also plays a role, as longer terms result in lower monthly payments but higher total interest costs. Additionally, making extra payments or refinancing can alter the amortization schedule.” } } ] }



