Is Accrued Interest Good Or Bad? Discover the Truth Behind It!
Accrued interest can be either good or bad depending on the situation.
Credit: www.fool.com
The Concept Of Accrued Interest
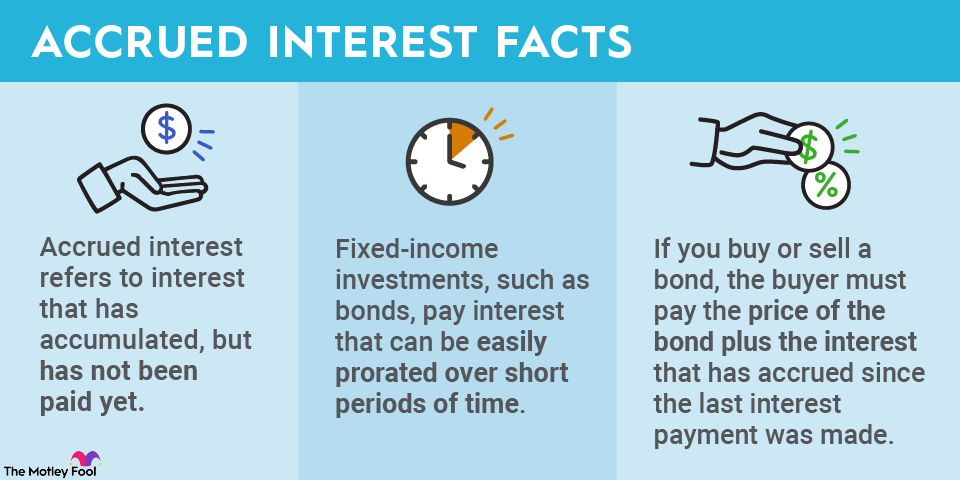
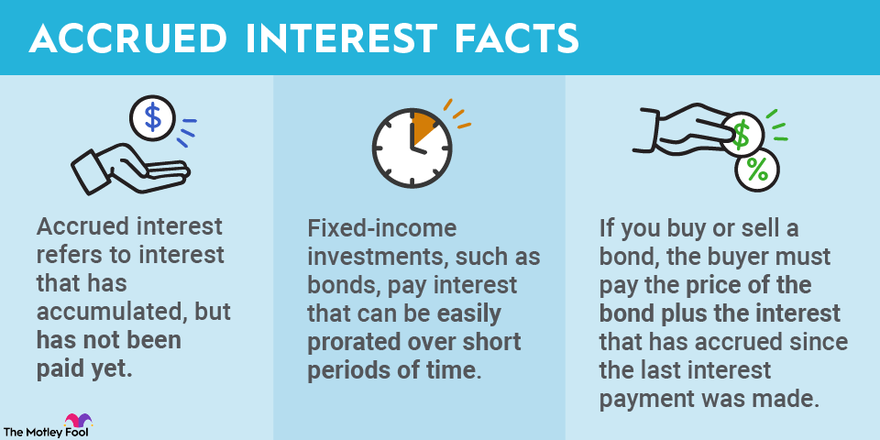
Accrued interest is a financial term that refers to the interest that has been earned but not yet paid or received. It is a concept that affects both borrowers and lenders, and understanding how it works is essential for anyone involved in financial transactions. In this article, we will explore the concept of accrued interest, its definition, and the different methods used to calculate it.
Definition
Accrued interest is the accumulation of interest on a financial instrument over time. It represents the amount of interest that has been earned but not yet paid or received. This can apply to various financial products such as loans, bonds, and certificates of deposit. For borrowers, accrued interest represents an additional cost they will have to pay at a future date. On the other hand, for lenders, accrued interest represents the income they will receive in the future.
Calculation Methods
There are different methods used to calculate accrued interest, depending on the type of financial instrument and the terms of the agreement. The most common calculation methods include:
- Straight-Line Method: This method evenly distributes the interest over the specified period, assuming a constant interest rate.
- Actual/Actual Method: This method calculates the accrual of interest on a day-by-day basis, taking into account the actual number of days in a year (leap year or non-leap year) and any relevant interest rate changes.
- 360/360 Method: This method assumes 360 days in a year and uses a simplified approach for calculating interest.
It is important to note that the specific method used may vary depending on the financial institution or the terms of the agreement. Borrowers and lenders should familiarize themselves with the calculation method applicable to their specific situation to ensure they have a clear understanding of the accrued interest amount.
Accrued interest is a fundamental concept in finance that has both positive and negative implications depending on one’s perspective. For borrowers, accrued interest represents an additional financial obligation, increasing the overall cost of borrowing. Lenders, on the other hand, view accrued interest as a source of income, reflecting the return on their investment. To make informed financial decisions, it is crucial to understand the concept of accrued interest and its implications.

Credit: www.discover.com
Pros And Cons Of Accrued Interest
Accrued interest, either on loans or investments, plays a significant role in the financial landscape. Understanding the pros and cons of accrued interest is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. In this section, we will explore both the advantages and disadvantages of accrued interest, helping you make informed decisions when it comes to managing your finances.
Advantages
Accrued interest can bring forth several benefits. Let’s take a look at some of the advantages:
- Additional Income: Accrued interest can lead to additional income for investors. When investing in instruments such as bonds or savings accounts, the interest earned can be a valuable source of extra money.
- Compound Interest: Accrued interest, when reinvested, can earn compound interest over time. This compounding effect can significantly boost the original investment or loan amount.
- Tax Deductions: In some cases, accrued interest on loans can be tax-deductible. This can help reduce the overall tax burden for individuals and businesses.
- Financial Flexibility: For businesses, accrued interest can provide financial flexibility by allowing them to invest or expand using borrowed funds while deferring the interest payments to a future date.
Disadvantages
However, accrued interest also has its drawbacks. Here are a few disadvantages to consider:
- Increased Debt: When it comes to loans, accrued interest can add to the overall debt burden. This means that individuals or businesses with loans will owe more than the initial amount borrowed.
- Reduced Cash Flow: Accrued interest payments can significantly impact cash flow, especially when dealing with large loan amounts. It is important to consider the effect on available funds before committing to accrued interest.
- Uncertain Future Rates: The interest rates in the future may not be as favorable as they are at the time of accrual. This uncertainty can affect the actual returns or payments on accrued interest.
- Complexity: Accrued interest calculations can be complex and require attention to detail. This added complexity may make it challenging for individuals or businesses to manage their finances effectively.
Implications For Investors
When it comes to investment decisions, accrued interest can have both positive and negative implications for investors. It is crucial for investors to understand the impact of accrued interest on their investments and consider the associated risks.
Impact On Investments
Accrued interest can be beneficial for investors, as it represents the amount of interest that has accumulated on a bond or other fixed-income investment since the last interest payment. This means that when an investor buys a bond, they will typically have to pay the seller the bond’s price plus the accrued interest since the last payment. The accrued interest becomes an additional return for the buyer, enhancing the bond’s yield. This can make the investment more attractive, especially when interest rates are low.
Risk Considerations
However, investors should also be aware of the risks associated with accrued interest. One important risk to consider is the potential impact of accrued interest on the bond’s price volatility. As the amount of accrued interest increases, the bond’s price may become more volatile, particularly if there are fluctuations in interest rates. This could lead to capital losses for investors if they need to sell the bond before the next interest payment date.
Managing Accrued Interest
When it comes to managing accrued interest, it’s essential to have a solid grasp of the strategies that can help mitigate its impact and the tax considerations that come with it. By understanding how to navigate these aspects, you can make better financial decisions and optimize your overall investment returns. In this section, we will explore some effective strategies for managing accrued interest and outline important tax considerations.
Strategies For Mitigation
1. Diversify Your Investments: One key strategy to minimize the impact of accrued interest is to diversify your investment portfolio. By spreading your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, you can reduce the risk of being overly exposed to a single investment’s accrued interest.
2. Invest in Tax-Advantaged Accounts: Another efficient way to manage accrued interest is to invest in tax-advantaged accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans. These accounts provide tax benefits that can help mitigate the impact of accrued interest on your overall tax liability.
3. Keep a close eye on interest rates: Monitoring interest rates is crucial when managing accrued interest. By staying informed about the current market rates, you can make informed decisions regarding your investments. If interest rates are expected to rise, you may want to consider allocating your investments accordingly to minimize the impact of accruing higher interest.
Tax Considerations
Understanding the tax implications of accrued interest is essential for effective management. Here are a few key considerations:
1. Tax on Interest Income: Accrued interest is generally taxable as ordinary income in the year it is earned. This means you’ll need to report the accrued interest on your annual tax return and pay tax accordingly. It’s crucial to keep accurate records of accrued interest for tax purposes.
2. Tax-Exempt Investments: Some investments, such as municipal bonds, offer tax-exempt interest. Investing in these types of securities can help reduce your overall tax burden on accrued interest. Be sure to explore the availability of tax-exempt investments when managing accrued interest.
| Tax Consideration | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Capital Gain Tax | When you sell an investment for a profit, you may be subject to capital gains tax on the accrued interest earned. Understanding the tax rates and rules surrounding capital gains will help you plan and manage your investments effectively. |
| Tax Deductibility | In some cases, accrued interest expenses may be tax-deductible. This is often applicable for investments related to business operations or rental property. Consult with a tax professional to maximize any potential tax deductions. |
By taking these tax considerations into account when managing accrued interest, you can optimize your financial position and avoid any potential tax pitfalls.
Accrued Interest In Different Financial Instruments
Accrued interest is an important concept in the world of finance. It refers to the interest that has been earned but not yet paid or received. Understanding how accrued interest works in different financial instruments can help investors make informed decisions. In this section, we will explore accrued interest in bonds and bank accounts, highlighting the key factors to consider for each.
Bonds
Bonds are a popular investment option for individuals and institutions alike. When you purchase a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer, such as a government or corporation. In return, you receive periodic interest payments known as coupon payments. Accrued interest plays a crucial role when buying or selling bonds before their maturity date.
When you buy a bond in the secondary market, you may have to pay accrued interest to the seller. This is because the interest accrues daily and belongs to the bondholder who owns the bond on that day. On the other hand, if you sell a bond before its maturity, you may be entitled to receive accrued interest from the buyer.
It’s important to note that accrued interest can significantly impact the purchase or sale price of a bond. This is especially true when there is a considerable time gap between interest payment dates. As an investor, it’s essential to consider the accrued interest component when evaluating bond prices and potential returns.
Bank Accounts
Bank accounts are another type of financial instrument where accrued interest comes into play. When you deposit money into a savings account or a certificate of deposit (CD), the bank pays you interest on your deposits. This interest accrues over time and is typically calculated on a daily or monthly basis.
In bank accounts, accrued interest is generally a positive aspect. It allows your money to grow over time without requiring any additional effort. The more time your money stays in the account, the more accrued interest you earn. This can be particularly beneficial for long-term savings goals, such as retirement or education funds.
It’s worth mentioning that different banks may have varying methods for calculating accrued interest. Some may compound interest daily, while others may compound it monthly or even annually. Additionally, certain types of bank accounts, like high-yield savings accounts, may offer higher interest rates, resulting in greater accrued interest.
In conclusion, accrued interest is neither inherently good nor bad. Its impact depends on the financial instrument being considered. For bonds, accrued interest can affect the purchase or sale price, while in bank accounts, it adds to the growth of your deposits. Understanding how accrued interest works in different financial instruments is crucial for making sound financial decisions.
Credit: www.fool.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Is Accrued Interest Good Or Bad?
What Is Accrued Interest And How Does It Work?
Accrued interest is the interest that has been earned but not yet paid or received. It is calculated based on the time period from the last interest payment to the current date. When you invest in bonds or borrow money, accrued interest plays a crucial role in determining the amount you will receive or owe.
Why Is Accrued Interest Important When Buying Or Selling Bonds?
Accrued interest is an integral part of bond trading. When buying or selling bonds, the purchaser pays the seller the market price plus the accrued interest. This ensures that the seller is compensated for the interest earned during their ownership period.
Buyers, on the other hand, pay accrued interest to account for the interest they will receive from the bond.
How Does Accrued Interest Affect Bond Prices?
Accrued interest impacts the price of a bond. As a bond approaches its interest payment date, the accrued interest increases, making the bond more valuable and hence, increasing its price. Conversely, as the interest payment date passes, the accrued interest decreases, resulting in a lower bond price.
Bond prices and accrued interest have an inverse relationship.
What Happens To Accrued Interest When A Bond Is Sold?
When a bond is sold, the accrued interest is typically paid to the seller. The buyer then assumes the responsibility of receiving the next interest payment. This ensures that both parties are compensated fairly for the interest earned during their respective holding periods.
Conclusion
Accrued interest can be beneficial as it allows investors to earn additional income. However, it also comes with some risks, such as potential cash flow challenges. Understanding the pros and cons of accrued interest is crucial for making informed financial decisions.
By weighing the advantages and disadvantages, individuals can effectively manage their investments.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is accrued interest and how does it work?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Accrued interest is the interest that has been earned but not yet paid or received. It is calculated based on the time period from the last interest payment to the current date. When you invest in bonds or borrow money, accrued interest plays a crucial role in determining the amount you will receive or owe.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Why is accrued interest important when buying or selling bonds?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Accrued interest is an integral part of bond trading. When buying or selling bonds, the purchaser pays the seller the market price plus the accrued interest. This ensures that the seller is compensated for the interest earned during their ownership period. Buyers, on the other hand, pay accrued interest to account for the interest they will receive from the bond.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does accrued interest affect bond prices?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Accrued interest impacts the price of a bond. As a bond approaches its interest payment date, the accrued interest increases, making the bond more valuable and hence, increasing its price. Conversely, as the interest payment date passes, the accrued interest decreases, resulting in a lower bond price. Bond prices and accrued interest have an inverse relationship.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What happens to accrued interest when a bond is sold?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “When a bond is sold, the accrued interest is typically paid to the seller. The buyer then assumes the responsibility of receiving the next interest payment. This ensures that both parties are compensated fairly for the interest earned during their respective holding periods.” } } ] }




