What is the Difference between Accrual And Amortization? Discover the Key Distinctions!
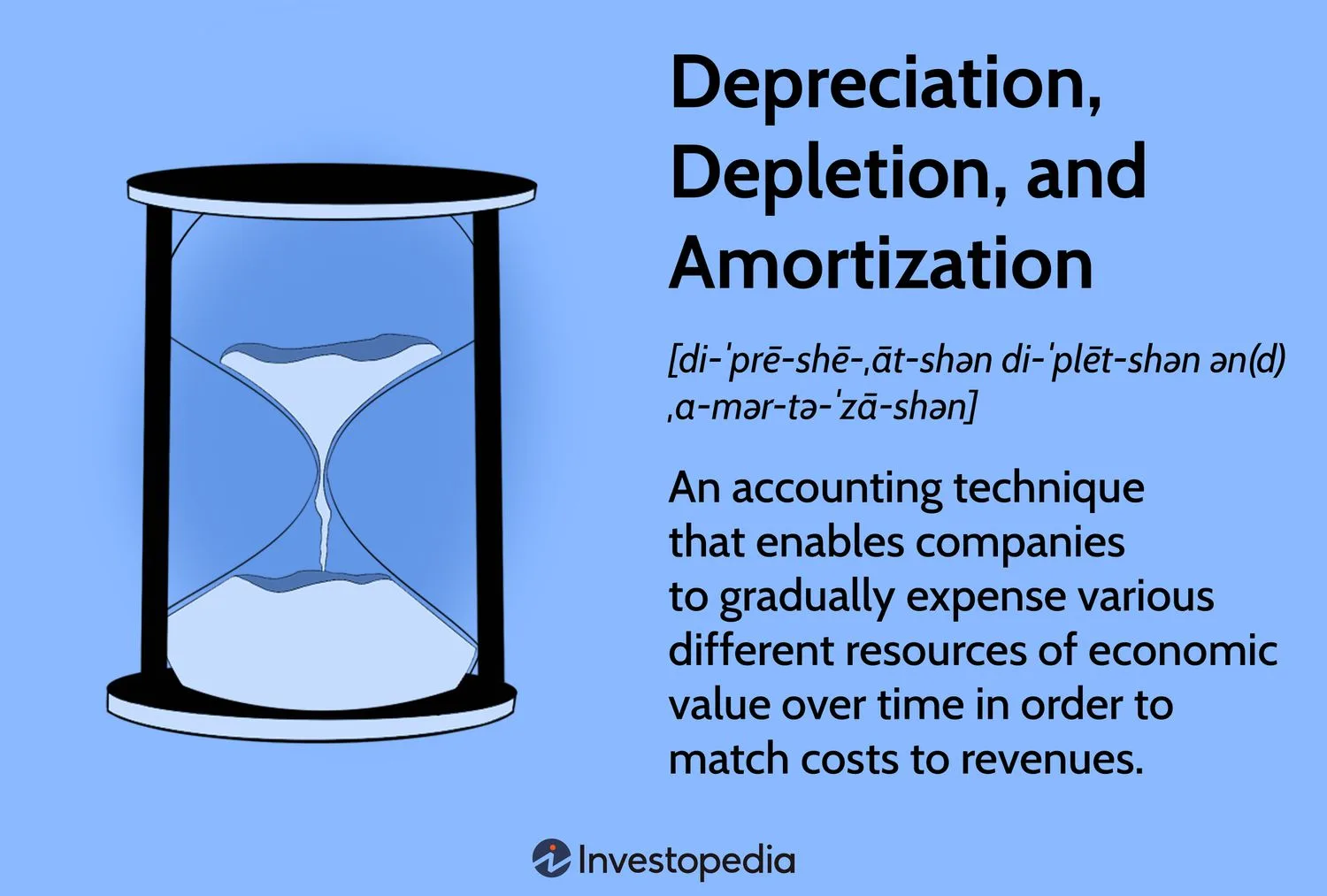
Accrual is the recognition of revenue or expenses when they are incurred, regardless of when they are received or paid. Amortization, on the other hand, refers to the gradual reduction of an intangible or a long-term liability over a specific time period.
Accrual and amortization are two distinct accounting concepts. Accrual involves recording revenue or expenses in the financial statements when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when the cash is received or paid. This method ensures that financial statements reflect the true financial position of a company.
On the other hand, amortization refers to the process of gradually reducing the value of an intangible asset (such as a patent or copyright) or a long-term liability (such as a loan or bond) over a specific period. This allows companies to allocate the cost or value of these assets or liabilities over their useful lives. Understanding the difference between accrual and amortization is crucial in financial reporting and analysis.
Credit: blog.netgain.tech
Accrual Vs. Amortization
Understanding the difference between accrual and amortization is essential for proper financial management. Both these accounting methods play a crucial role in recognizing expenses and revenues. In this article, we will delve into their definitions, applications in the accounting field, timing of recognition, financial statement impact, and tax implications.
Definition
Accrual and amortization are terms commonly used in accounting to allocate expenses and revenues over a specific period of time. Let’s take a closer look at each:
| Accrual | Amortization |
|---|---|
| Accrual refers to the process of recognizing expenses or revenues when they are incurred, regardless of when the cash is actually received or paid. | Amortization, on the other hand, is the method of allocating the cost of an intangible asset or a liability over its useful life. |
Application In Accounting
Accrual accounting is widely used to provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position. This method allows expenses and revenues to be matched in the same accounting period, regardless of when the cash transactions occur. It enables businesses to have a better understanding of their financial performance and aids in decision-making processes.
Amortization, on the other hand, is applied when there is an intangible asset to be recorded or when a liability needs to be settled over time. Examples of intangible assets include copyrights, trademarks, and patents. By allocating the cost of these assets over their useful life, amortization allows for a more accurate representation of their value in the financial statements.
Timing Of Recognition
Accrual and amortization differ in terms of when the recognition of expenses and revenues takes place:
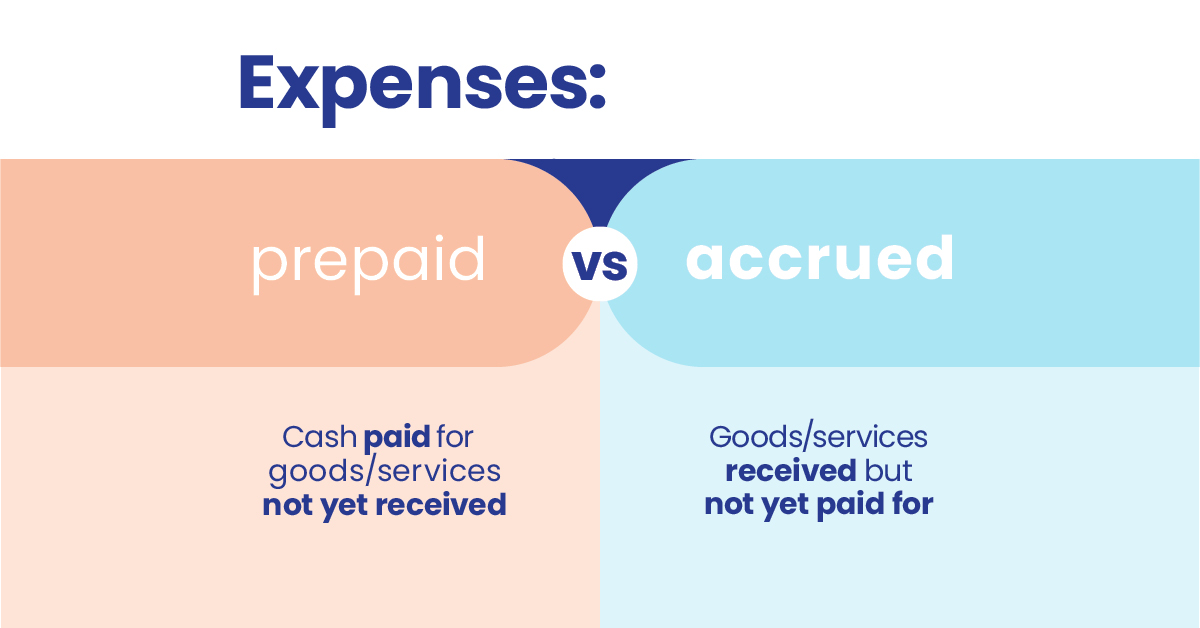
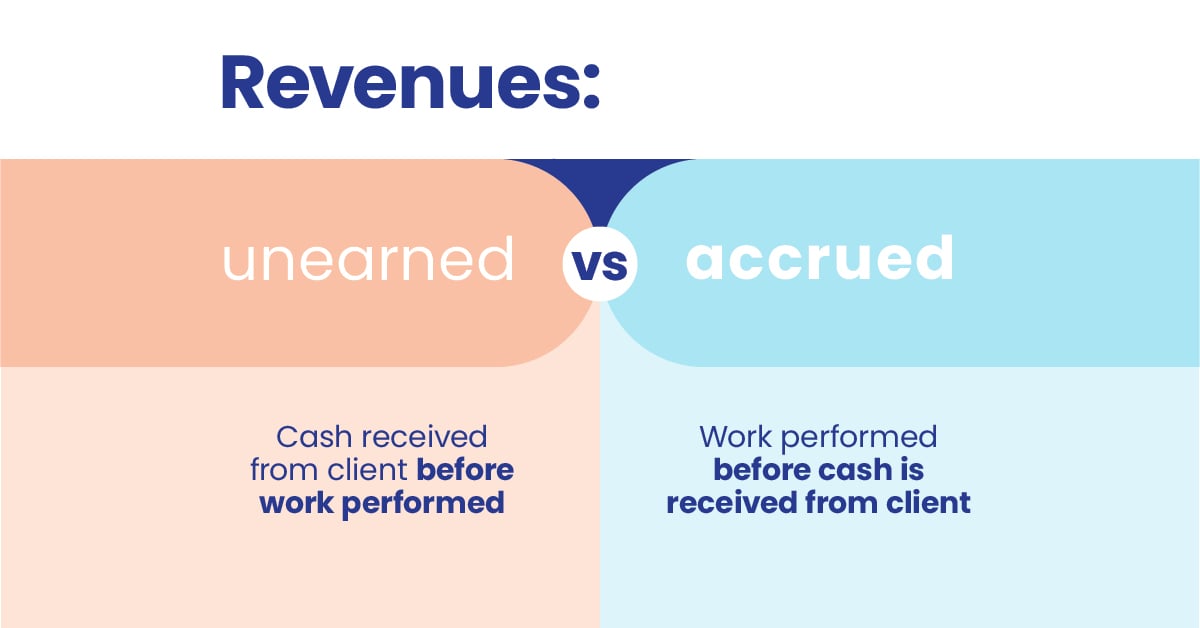
- Accrual: Expenses and revenues are recognized when they are incurred, regardless of cash inflows or outflows. This ensures that financial statements reflect the economic reality of a business.
- Amortization: The allocation of the cost of an intangible asset or a liability occurs over its useful life. This gradual recognition helps spread the expenses or revenue impact evenly over time.
Financial Statement Impact
The impact on financial statements is another area where accrual and amortization diverge:
- Accrual: By recognizing expenses and revenues when they occur, the financial statements provide a more accurate reflection of a company’s financial performance. It allows for a better assessment of profitability, asset value, and overall financial health.
- Amortization: The gradual recognition of the cost of an intangible asset or a liability helps spread the impact over time, resulting in more stable and predictable financial statements.
Tax Implications
Accrual and amortization can also have different tax implications:
- Accrual: Expenses are deductible in the year they are accrued, even if the payment is made in a different year. This means businesses may need to account for expenses that they have yet to pay.
- Amortization: Depending on the tax regulations and the type of asset or liability being amortized, different rules and rates may apply. It’s essential to understand the applicable tax laws to ensure proper compliance.
By understanding the difference between accrual and amortization and their respective applications, timing of recognition, impact on financial statements, and tax implications, businesses can accurately record and report their financial activities. Proper utilization of these accounting methods ensures transparency, accuracy, and compliance.
Credit: blog.netgain.tech

Credit: synder.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Difference Between Accrual And Amortization?
What Is Accrual?
Accrual refers to the accounting method where transactions are recorded when they occur, regardless of when the actual payment is made. It helps provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position.
What Is Amortization?
Amortization is the process of gradually paying off a debt over a specific period of time. It involves periodic payments that include both principal and interest until the entire debt is fully repaid.
How Does Accrual Differ From Amortization?
Accrual and amortization are two different concepts in accounting. Accrual focuses on recording revenue or expenses when they are earned or incurred, while amortization focuses on the gradual repayment of debts or the reduction of assets over time.
Why Is Accrual Important In Accounting?
Accrual is important in accounting because it helps provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position. It ensures that revenue and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, giving a more realistic view of the company’s performance.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between accrual and amortization is essential for managing your finances effectively. These accounting methods play crucial roles in tracking income and expenses over time and can significantly impact your financial reports. By grasping these concepts, you can make more informed decisions and improve the overall health of your business.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is accrual?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Accrual refers to the accounting method where transactions are recorded when they occur, regardless of when the actual payment is made. It helps provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is amortization?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Amortization is the process of gradually paying off a debt over a specific period of time. It involves periodic payments that include both principal and interest until the entire debt is fully repaid.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How does accrual differ from amortization?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Accrual and amortization are two different concepts in accounting. Accrual focuses on recording revenue or expenses when they are earned or incurred, while amortization focuses on the gradual repayment of debts or the reduction of assets over time.” } } , { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Why is accrual important in accounting?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Accrual is important in accounting because it helps provide a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position. It ensures that revenue and expenses are recorded when they are earned or incurred, giving a more realistic view of the company’s performance.” } } ] }