What is the Difference between Loan Term And Amortization? Explained
The loan term refers to the length of time in which a loan must be repaid, while amortization refers to the process of gradually paying off a loan over time through regular payments that cover both the principal and interest. The loan term specifies the duration of the loan, such as 5 years or 30 years, while amortization determines the schedule of payments required to fully repay the loan.
Loan term and amortization are important factors to consider when borrowing money, as they affect the overall cost of the loan and the monthly repayment amount. Understanding the difference between these two terms is crucial for individuals seeking loans to make informed financial decisions.
Loan Term And Amortization
Loan term and amortization are two different concepts in the world of loans. Loan term refers to the duration of the loan, while amortization is the process of gradually paying off the loan through regular installments. Understanding the distinction between the two is crucial when considering borrowing options.
When taking out a loan, one of the important factors to consider is the loan term. The loan term refers to the duration or length of time that a borrower has to repay the loan in full. In simpler terms, it is the time period over which you are obligated to make regular loan payments until the loan is completely paid off. The loan term can vary depending on the type of loan, from a few months to several years.
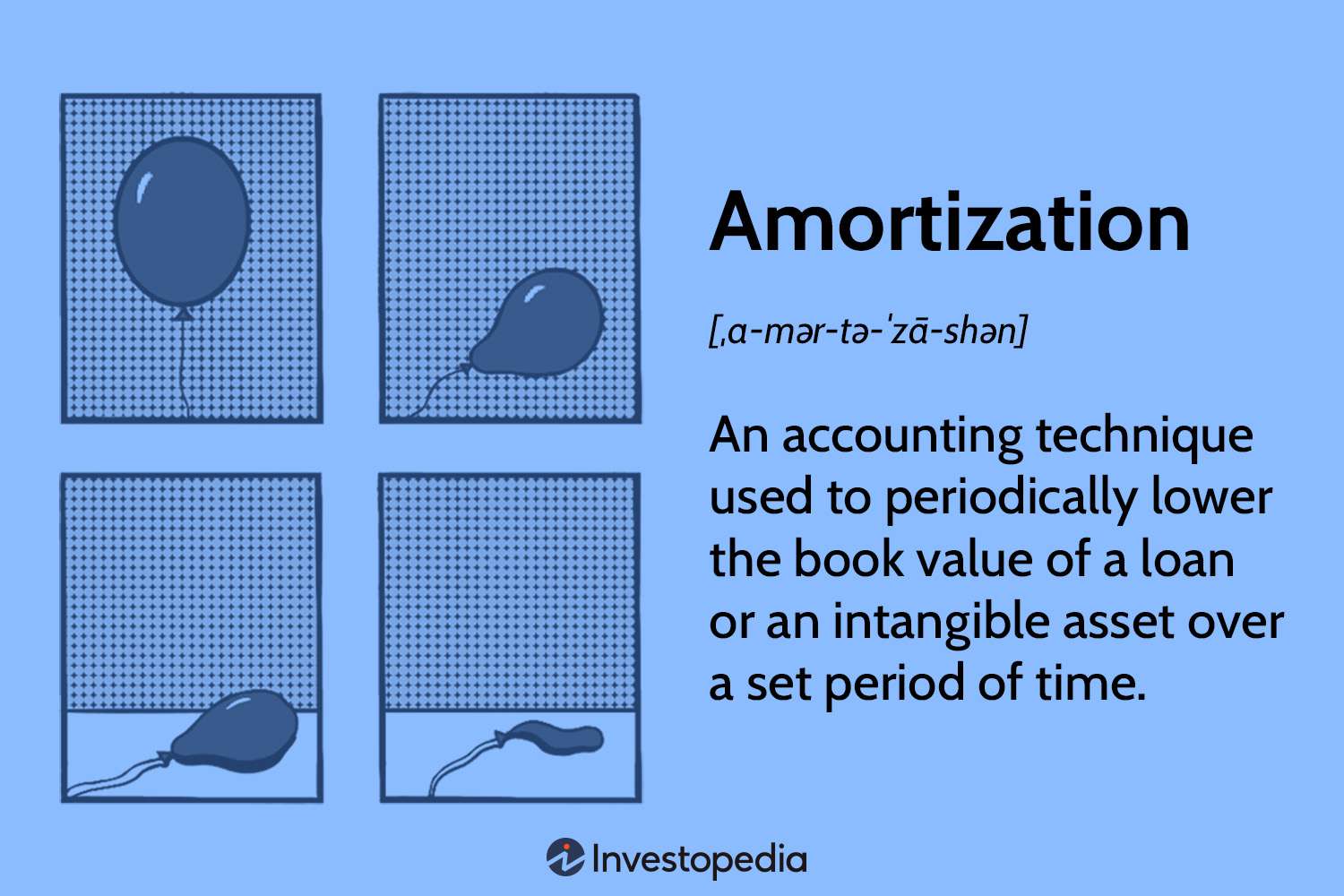
Amortization, on the other hand, is the process of gradually paying off a loan through regular installment payments that cover both the principal amount and the interest. Each installment payment is divided between reducing the loan balance (the principal) and paying the interest that has accrued over time. As the loan term progresses, the portion of the payment allocated to the principal increases, while the interest portion decreases.
Amortization is a common method used by lenders to ensure that the loan is repaid in a structured manner over the agreed loan term. It allows borrowers to gradually reduce their outstanding debt while keeping their monthly payments manageable.
Difference Between Loan Term And Amortization
The main difference between loan term and amortization is that the loan term refers to the overall length of time that a borrower has to repay the loan, while amortization refers to the gradual repayment of the loan through regular installments, taking into account both the principal and interest.
Here’s a simplified explanation:
| Loan Term | Amortization |
|---|---|
| Refers to the overall length of time to repay the loan | Refers to the gradual repayment of the loan through regular installments |
| Can vary depending on the type of loan | Incorporates both the principal and interest into the installments |
| Does not necessarily indicate the repayment structure | Ensures a structured repayment plan over the loan term |
In conclusion, while loan term and amortization are interconnected, they refer to different aspects of the loan. The loan term represents the duration of the loan, while amortization is the method used to gradually repay the loan through regular installments. Understanding these concepts can help borrowers make informed decisions when seeking financing options.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/amortized_loan.asp-final-23646fe3883e4f87902df8207a750e0a.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Loan Term
When it comes to understanding loan agreements, two terms that often cause confusion are loan term and amortization. In this blog post, we will focus on loan term and provide a clear definition as well as explain the impact it has on monthly payments.
Definition
Loan term refers to the period of time a borrower has to repay a loan in full, including principal and interest. It is usually expressed in months or years, depending on the terms of the loan agreement. For example, a common loan term for a mortgage is 30 years.
Impact On Monthly Payments
The length of the loan term plays a significant role in determining the amount of the monthly payments. Typically, loans with shorter terms have higher monthly payments, while those with longer terms have lower monthly payments.
This can be attributed to the fact that with shorter loan terms, the borrower has less time to repay the loan, so the payments need to be higher in order to satisfy the loan agreement within the specified timeframe.
On the other hand, longer loan terms allow for smaller monthly payments since the repayment period is extended. Although this may seem attractive, it is important to note that longer loan terms often result in paying more interest over the life of the loan.
To illustrate this, let’s consider a hypothetical example:
| Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Loan Term | Monthly Payment | Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $200,000 | 4% | 15 years | $1,479.38 | $66,288.95 |
| $200,000 | 4% | 30 years | $954.83 | $143,739.01 |
In the example above, we can observe that by choosing a 30-year loan term instead of a 15-year term, the monthly payment is significantly lower. However, over the life of the loan, the borrower ends up paying more than double the amount of interest.
Therefore, it is crucial for borrowers to carefully consider the loan term and assess their financial capabilities before entering into a loan agreement.
Amortization
Definition
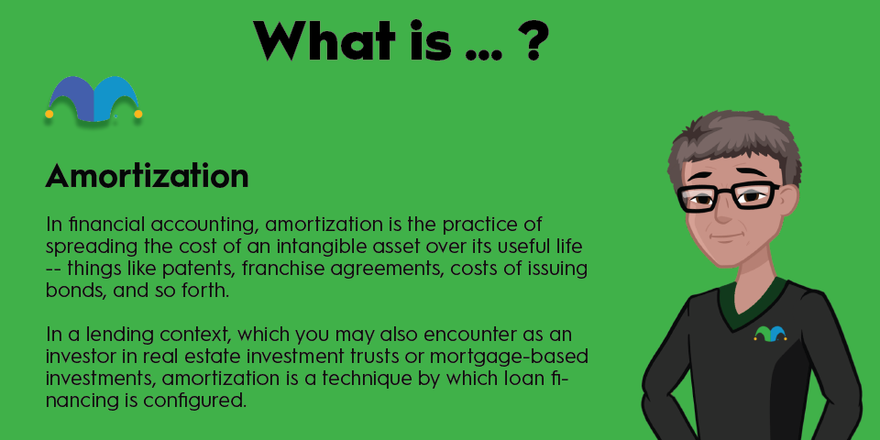
Amortization refers to the process of spreading out loan payments over time, with a portion of each payment going towards both the principal amount and the interest. This means that with each payment, the loan balance is reduced, allowing the borrower to pay off the debt gradually.
Effect On Total Interest Paid
Amortization significantly affects the total interest paid over the life of a loan. In the early stages of a loan, a larger portion of each payment goes towards interest. As the loan progresses, a higher percentage goes towards the principal, reducing the overall interest paid.

Credit: financelobby.com
Credit: www.fool.com
Frequently Asked Questions On What Is The Difference Between Loan Term And Amortization?
What Is The Difference Between Loan Term And Amortization?
The loan term refers to the length of time it takes to repay a loan, while amortization refers to the process of gradually paying off the principal amount and the interest on the loan through regular payments. In simple terms, the loan term is the duration of the loan, while amortization is the method used to repay it.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between loan term and amortization is crucial for managing your finances. By comprehending the distinct concepts, you can make informed decisions about your loans. Knowing how the loan term and amortization work will help you budget and plan for your financial future more effectively.
Being knowledgeable about these terms gives you a clearer picture of your financial responsibilities.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is the difference between loan term and amortization?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “The loan term refers to the length of time it takes to repay a loan, while amortization refers to the process of gradually paying off the principal amount and the interest on the loan through regular payments. In simple terms, the loan term is the duration of the loan, while amortization is the method used to repay it.” } } ] }